User interface design (UI design) focuses on creating visually appealing and personalized interfaces. The primary goal of a UI designer is to develop an interface that is both user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing. To achieve this, designers must consider all possible user interactions with the product and provide optimal solutions that make these interactions meaningful.
Following an iterative design process is essential for continuously improving and refining designs. A structured design process enables the creation of simple and intuitive interfaces that satisfy users, setting your products apart from competitors.
What is user interface design?
Every human-centered design project begins with the user interface (UI) design process. Designers use this process to create pages or products that stand out in the market. UI design serves as the front face of your product, acting as a bridge between the user and the product's functionality.
A successful UI design requires a solid understanding of UI elements and controls such as buttons, menus, text boxes, lists, dialogs, and icons. By thoughtfully combining these elements, designers create products that attract users through their look and feel.
Why user interface design is important?
Users primarily care about the functionality of a product. If they can perform their desired tasks easily, they are satisfied with the product's design. Therefore, a minimalistic and intuitive design is crucial. Users want to quickly locate the options and elements they need to complete tasks efficiently. Designing customer journey maps helps provide a seamless experience that meets user expectations.
A pleasant UI design fosters user trust. By delivering a personalized experience, you can build user loyalty. Consistent brand messaging through the UI design also strengthens user confidence and fosters positive brand perceptions.
7 Step Process of UI Design
After thorough user research by a team of designers, developers, and product managers, the UI design process unfolds in the later stages of product development. Integrating appropriate styles and interactions to create an optimal user experience builds upon the groundwork laid by the UX design process.
While the steps below are presented linearly, it's important to note that iteration between phases may be necessary based on testing and user feedback.
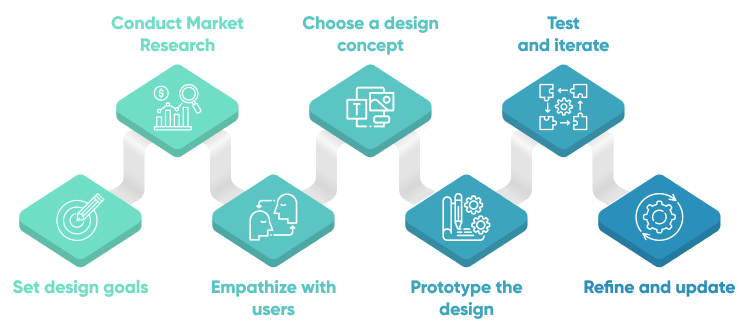
Set design goals
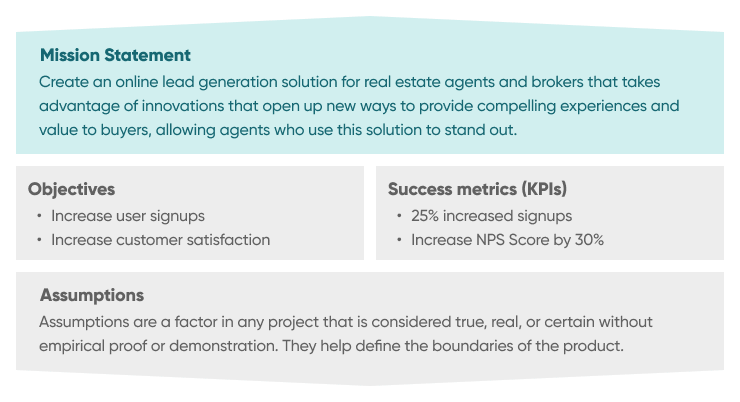
The first step in the UI design process is to define the goals your team aims to achieve. Design solves problems, so understanding the problem is crucial before providing a solution. Design teams rely on design briefs—a document outlining all essential components of the design project. The design brief serves as the project's backbone and a communication tool between the customer and designer, offering insights into user needs and the type of design that will fulfill those needs.
Highlight goals and objectives
Clearly state the purpose of the design. Explain what the design aims to achieve. Without clear objectives, designers risk creating something that clients may not find useful. A well-prepared design brief serves as a foundational document ensuring every UI design aspect is aligned with these goals. This alignment guarantees that the UI not only looks appealing but also drives meaningful business results.
Analyze business metrics and KPIs
Investors and business owners focus on metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) that demonstrate the effectiveness of UI design. Analyzing metrics like conversion rates, user engagement, and customer satisfaction provides insights into how the UI impacts business performance. This data-driven approach ensures that design decisions are based on tangible business outcomes.
Scope
Detail what the project will cover. Specify whether it's a new website or application or enhancements to an existing product. A clear scope directs designers' efforts effectively, saving time and resources.
Success Criteria
Include key performance indicators (KPIs) and objectives that define a successful product. These metrics help measure the effectiveness of the design in meeting business goals.
Project Team
Outline the team involved in the project, detailing each member's tasks and responsibilities, as well as stakeholder roles.
Deadline
Set a realistic delivery date after consulting with the client. A clear deadline ensures timely completion and helps avoid potential delays.
 Read More: Product Charter: Template & Writing Process Steps
Read More: Product Charter: Template & Writing Process Steps
Conduct market research
Understanding the market and your competitors is key to designing a standout UI. By analyzing competitors' UI designs, you can see what works well, identify gaps, and find ways to make your interface unique. This helps you create designs that not only look good but also meet user needs effectively. Additionally, knowing your client's business model, goals, and challenges ensures that the UI aligns with their strategic objectives, enhances user engagement, and supports business growth.
Understand users
Your most important task is to understand what exactly the user wants from your product. You can do this by taking feedback from users regularly. Meet users and ask questions about what they want to achieve using your product. Observe them in their working environment and see how they handle their daily problems. This will give you a good understanding of what users think and you will design your product accordingly.
Analyze competitors
A comprehensive understanding of the market and competitive landscape is essential. Analyzing competitors' UI designs helps identify industry standards, emerging trends, and opportunities for differentiation. This knowledge enables designers to create unique and competitive interfaces that stand out in the market.
Leverage data and AI
AI tools like ChatGPT can analyze online data such as user reviews, forum discussions, and social media interactions to extract valuable insights about user behaviors, preferences, and pain points. This enables designers to gain a comprehensive understanding of their target audience without direct user engagement.
Incorporating AI into your research process enhances the depth and accuracy of your insights, ensuring your UI design remains user-centric even without direct access to end-users.
PRO TIP: Leverage AI to streamline your competitor analysis by performing advanced web searches and synthesizing the information. Input specific industry-related keywords and queries into ChatGPT to identify both direct and indirect competitors. ChatGPT can help summarize competitors' UI features, highlight their strengths and weaknesses, and provide insights on market positioning.
Define your search criteria:
Determine the keywords relevant to your industry and product offerings. This could include specific functionalities, target audience demographics, or unique selling points.
Input queries into ChatGPT:
Ask ChatGPT to identify competitors by using queries such as:
- "How do competitors position themselves?"
- "What do competitors' designs look and feel like?"
- "Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of [competitor names]."
Analyze summarized data:
Review the summaries provided by ChatGPT to understand each competitor’s UI design elements, user experience strategies, and market positioning.
Empathize with users
Empathizing with users is essential for successful UI design. It means understanding their needs and challenges to create effective solutions. For example, designing a tool for doctors requires knowing their specific requirements, such as managing patient records and scheduling appointments. User research helps identify user problems and behaviors. By putting themselves in users' shoes, designers gain insights into how users think and interact with products, leading to more user-centered designs.
Tools and methods to understand users:
Personas
User personas are fictional representations of your ideal users, detailing their demographics, behaviors, goals, and challenges. Creating accurate personas is crucial for developing user-centric designs. When direct access to users is unavailable, AI tools like ChatGPT can generate these personas by synthesizing data from various online sources. By inputting specific criteria and user data into AI chat, designers can receive well-structured and insightful personas that reflect different segments of their target audience.
PRO TIP: Use the power of ChatGPT to generate detailed user personas from your research data. By inputting your collected user information, AI can analyze demographics, behaviors, and preferences to create comprehensive and accurate personas. This not only saves time but also ensures that your UI design is closely aligned with your target audience's needs and expectations.
How to implement:
- Input data into chat: Provide ChatGPT with the gathered data, specifying key details such as user demographics, behaviors, goals, and pain points.
- Generate personas: Ask ChatGPT to synthesize the information into structured user personas, highlighting essential characteristics and motivations.
- Refine and customize: Review the generated personas and make any necessary adjustments to ensure they accurately represent your target users.
- Integrate into design process: Use these personas to guide your UI design decisions, ensuring that the interface meets the actual needs and preferences of your users
Scenarios
Scenarios help bridge the gap between user research and design implementation by providing context for how your interface will be used. They bring user personas to life and guide design decisions by focusing on specific, relatable use cases.
Here are a few examples of scenarios that could guide the design process for different products:
- Fitness App Scenario: Maria is a busy professional who uses her fitness app to track her workouts. During her lunch break, she opens the app to log a quick workout and review her progress for the week. She needs a clear, distraction-free interface that allows her to accomplish these tasks in under two minutes.
- Financial App Scenario: Peter, a freelance graphic designer, wants to quickly transfer money to her savings account while at a coffee shop. She expects the app to load fast, display her account balances clearly, and complete the transaction in a few taps.
PRO TIP: When creating scenarios, consider the following tips:
- Focus on your user personas and their specific goals.
- Describe the environment or context in which the scenario takes place.
- Highlight the tasks the user wants to complete and any potential challenges they might face.
- Keep scenarios concise but rich in detail to make them relatable and actionable.
By crafting detailed scenarios, you can ensure that your UI design aligns with real-world user needs and delivers a seamless, satisfying experience.
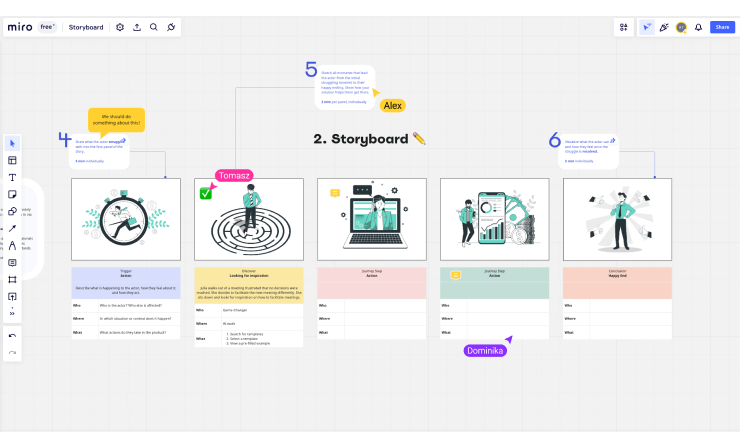
Storyboard
A storyboard allows you to create a low-fidelity visual representation focusing on users and their actions, thoughts, goals, emotions, and relationships. It outlines a specific situation or scenario and the sequence of actions a user will take to complete it. Sharing storyboards with stakeholders facilitates feedback and idea improvement.
Choose a design concept
At this stage, the UI designer begins crafting the digital product’s graphical user interface. This involves defining layouts, deciding on information architecture, creating icons, selecting color themes, defining typography styles, and setting UI guidelines.
Ideation map
Ideation is the process of generating and evaluating various ideas to find effective solutions. By organizing positive and negative aspects of ideas, designers can identify problems and develop successful solutions. A visual ideation map helps in structuring these thoughts, making it easier to decide on the best solution by listing negative feelings on one side and positive feelings on the other.
Moodboard
A moodboard defines the visual look of your product design. By combining images, styles, text, colors, and icons, you can present the product layout to a wider audience, helping them understand the product's purpose. Creating multiple moodboards and gathering audience feedback allows you to select the best one that resonates with your target audience.
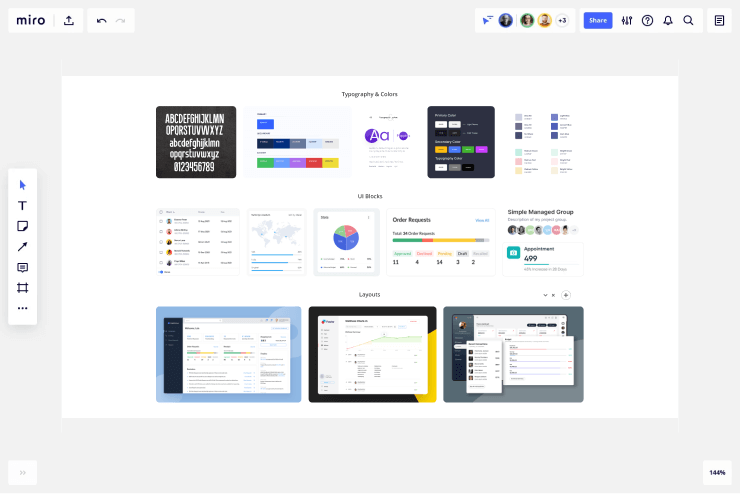
Prototype the design
With screen layouts defined, the team begins design work through sketches. Paper sketches, whiteboard flows, and wireframes help share design ideas with stakeholders early in the process, facilitating feedback and multiple iterations. The objective is to create a usable design that achieves user satisfaction.
Flowcharts
User flowcharts represent the sequence of screens a user navigates through to perform specific tasks. Starting from an entry point like a homepage or login screen and ending with the completion of a process, user flows help designers visualize the user experience.
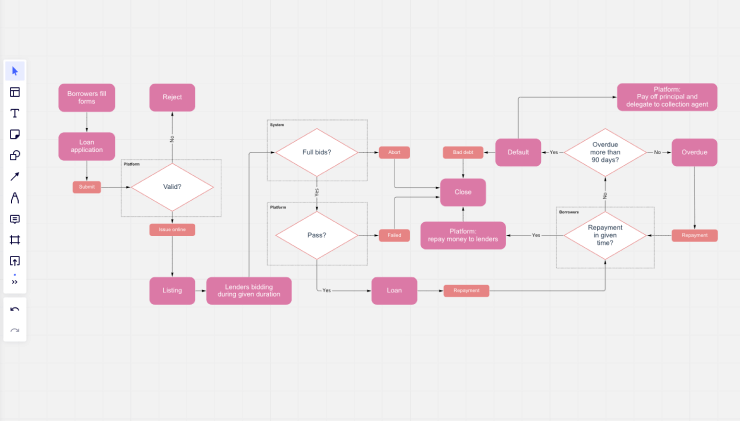
Wireframes
Wireframing involves creating a skeleton of the digital product, outlining which interface elements will appear on crucial pages. This essential UI design process can be performed using tools like Figma, Sketch, Axure, and Balsamiq. After wireframing, designers can create high-fidelity mockups with detailed color themes and link screens in prototyping tools like Figma, Sketch, and Adobe XD to visualize the product design similar to the working product.
Test and iterate
Once the prototype is ready, the team can conduct usability testing to gather feedback from actual users. Unlike QA testing and A/B testing, usability testing focuses on user-friendliness and whether users can accomplish their objectives using the product.
After successful usability testing, designers document and evaluate the results. Various types of usability testing include:
- Comparative usability testing: Compare two products (possibly competitors) or two versions of a single product (A/B testing) to identify their strengths and weaknesses. This helps choose the best option based on real user needs.
- Explorative usability testing: Conducted during early design stages, this testing explores different design ideas to identify flaws and gaps. It helps pinpoint market demands before product release.
- Usability evaluation: Performed after essential modifications and product launch, this testing ensures the product positively impacts users, confirming their satisfaction with functionality and experience.
Following user testing, designers iterate on UI and UX design before handing off to the development team. Designers support the implementation process, audit the implemented UI, identify gaps, and continue refining the experience post-launch.
Always be prepared to loop back to the design phase with fresh insights — the goal is to create a user experience that feels intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable to your end users.
Read More: 10 Proven Steps to Quickly Write a QA Test Plan

Refine and update
After product release, when users begin using it and achieving their goals, UI/UX designers continue their work to keep the product updated with new UI and UX design trends.
Further testing
Post-launch, continue testing to ensure key functions work well and identify usability improvements. Observe user interactions, document outcomes, and reiterate different options based on A/B testing results to release the best version.
Improvements and new features
Stay updated with new trends and understand evolving user needs due to technological advancements. Update feature sets and design new features within existing products to meet changing user demands.
While the design process stages and deliverables listed above are commonly used, they can be customized based on requirements. Deliverables at each stage can be adjusted or skipped if not needed. The ultimate goal is to achieve the desired user experience and satisfaction.
Conclusion
UI design involves the interaction between users and digital products, such as mobile apps or websites. It emphasizes aesthetics and personalization to create interfaces that are both attractive and functional.
A well-designed interface plays a crucial role in attracting and retaining users. If users enjoy interacting with your product and feel comfortable completing their tasks, you've successfully designed a good product.
The UI design process comprises several stages: setting design objectives, conducting user research, understanding your client's business, empathizing with users by creating personas and empathy maps, defining user scenarios, designing the graphical user interface, prototyping, testing and iterating, and refining and updating the product. This iterative approach ensures user satisfaction and helps retain existing users while attracting new customers in a competitive market.




![How to Design a SaaS Product Users Will Love [with examples]](/uploads/blog/saas-design/saas-design.png)